Insect bites or stings are not usually serious and get better in a few days. But sometimes they can become infected or cause a serious allergic reaction.
Bites from some insects can also cause illnesses, such as Lyme disease from ticks, scabies from mites, and malaria from mosquitoes in certain parts of the world.
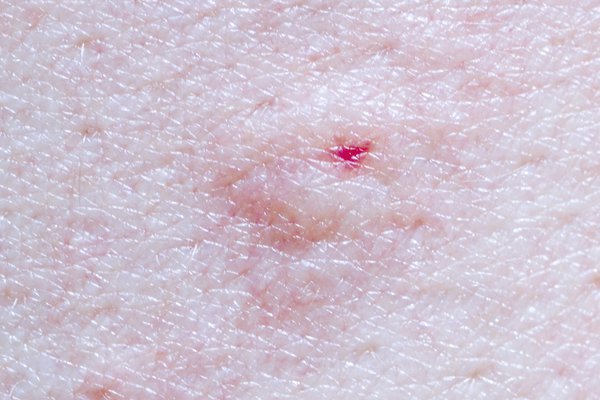
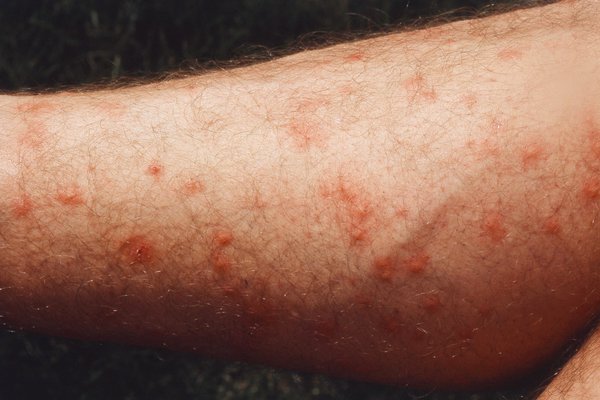
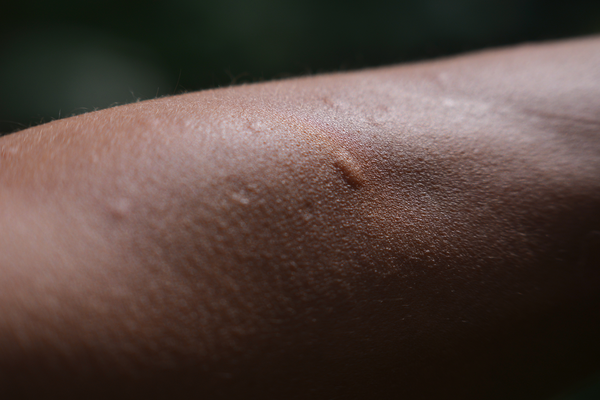
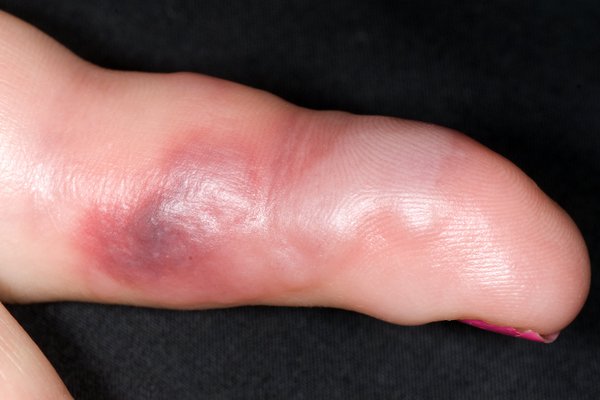
The main symptoms of an insect bite or sting are:
- pain where you were bitten or stung
- a small, swollen lump on the skin
The lump may look red. It may be more difficult to see on black or brown skin, but you should be able to feel it.
If you're not sure it's an insect bite or sting
You can often treat an insect bite or sting without seeing a GP.
Removing stingers, ticks or caterpillars
If anything is left on or in your skin, the first thing you need to do is remove it carefully.
If there's nothing in your skin, or you've removed it, wash your skin with soap and water to help lower the chance of infection.
The bite or sting should get better in a few days. There are some things you can do to ease your symptoms.
Do
put an ice pack wrapped in a cloth or a clean cloth soaked in cold water on the bite or sting for at least 20 minutes, if it's swollen
keep the area raised if you can
take painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen if the sting is painful
use antihistamines to relieve any itching (but do not use antihistamine cream if you had caterpillar hairs on your skin)
use a hydrocortisone cream to reduce itching and swelling
Don't
do not scratch the bite or sting, as it could get infected
do not use home remedies such as bicarbonate of soda to treat the bite or sting
A pharmacist can advise you about medicines that can help ease the symptoms of a bite or sting, such as:
- antihistamines
- steroid creams
- painkillers
They can also provide other treatments if you need them, without you seeing a GP.
Ask for an urgent GP appointment or get help from NHS 111 if:
You've been bitten or stung by an insect and:
- your symptoms get worse or are not getting any better
- you were stung in your mouth or throat, or near your eyes
- you have tummy pain and are being sick
- you feel dizzy or lightheaded
- a large area around the bite or sting becomes red and swollen
- you have a high temperature and swollen glands
- you were stung more than once
- you've had a serious allergic reaction to an insect bite or sting before
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Call 999 if:
- your lips, mouth, throat or tongue suddenly become swollen
- you're breathing very fast or struggling to breathe (you may become very wheezy or feel like you're choking or gasping for air)
- your throat feels tight or you're struggling to swallow
- your skin, tongue or lips turn blue, grey or pale (if you have black or brown skin, this may be easier to see on the palms of your hands or soles of your feet)
- you suddenly become very confused, drowsy or dizzy
- someone faints and cannot be woken up
- a child is limp, floppy or not responding like they normally do (their head may fall to the side, backwards or forwards, or they may find it difficult to lift their head or focus on your face)
You or the person who's unwell may also have a rash that's swollen, raised or itchy.
These can be signs of a serious allergic reaction and may need immediate treatment in hospital.
Bournemouth
Dorset
BH4 9HJ
